Strokes are currently the fifth leading cause of death in the US, killing one person every 4 minutes. To put this in perspective, every 40 seconds someone in the US suffers a stroke. What are stroke prevention methods in Manhattan NY? Go in for a stroke screening.
Stroke screenings are exams that identify the early warning signs of a stroke. These exams help prevent strokes before they happen, increase the chance of recovery after they occur, and stop any recurring attacks. To get the best results from the exam, you need to find a stroke specialist.
Let’s go over the different types of stroke screening as well as the different types of strokes so you’ll be better prepared to make an informed decision.
Stroke Prevention: Manhattan NY: Causes and Risks
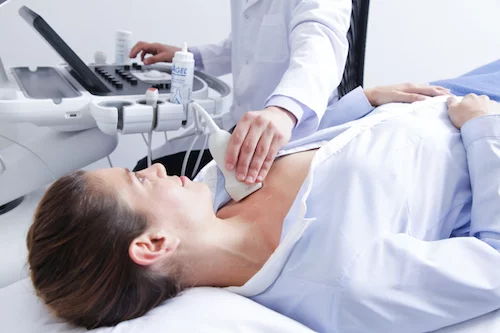
 You suffer a stroke when your brain stops functioning partially or completely. A stroke is essentially an attack on the brain and is characterized by a lack of blood flow due to vessel blockage. When this happens, insufficient oxygen reaches the brain and brain cells start to die.
You suffer a stroke when your brain stops functioning partially or completely. A stroke is essentially an attack on the brain and is characterized by a lack of blood flow due to vessel blockage. When this happens, insufficient oxygen reaches the brain and brain cells start to die.
There are two types of strokes: ischemic and hemorrhagic. Ischemic strokes occur when a blood vessel blockage in the brain caused by a blood clot leads to a stroke. This is the most common type of stroke, accounting for 87% of all stroke cases. A stroke screening test for ischemic stroke risk looks for two types of obstruction:
- Cerebral thrombosis – this is when a blood clot (or thrombus) appears on the blocked part of the blood vessel.
- Cerebral embolism – where a clot in another part of the body breaks off and travels to small blood vessels in the brain, blocking passage. This can be caused by atrial fibrillation (an irregular heartbeat).
A third of all ischemic strokes are considered cryptogenic, meaning the cause is unknown or obscure. And cryptogenic strokes are difficult to identify during a stroke screening exam.
On the other hand, a hemorrhagic stroke occurs as a result of blood leakage in the brain due to a ruptured vessel. This type of stroke can be caused by uncontrolled hypertension (causing intracerebral hemorrhage) or a burst aneurysm (causing subarachnoid hemorrhage). It accounts for about 13% of all strokes, according to the American Stroke Association.
It is also possible to suffer a mini-stroke, or a Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA). This could be caused by reduced blood flow in a major artery, a narrowed blood vessel in the brain, or when a blood clot in the body travels to the brain. TIAs aren’t fatal but can lead to recurrent stroke attacks in the future.
Common stroke symptoms
A stroke hits suddenly when it happens, without any notable warning signs or symptoms. However, there are some warning signs associated with the disease. When detected early enough, a stroke can be prevented. These early warning signs include:
- Sudden difficulty in speaking or loss of speech altogether
- Dizziness and losing balance
- Loss of or blurred vision
- An abrupt severe headache
- Sudden numbness of the face, arms, legs or one body side
- Abrupt loss of memory
How is stroke screening done?
 There are various stroke screening tests that can be carried out to determine the likelihood of a possible attack. Most of these assessments are based on the patient’s risk factors. So, before we discuss the different tests, here are the major risk factors for a stroke:
There are various stroke screening tests that can be carried out to determine the likelihood of a possible attack. Most of these assessments are based on the patient’s risk factors. So, before we discuss the different tests, here are the major risk factors for a stroke:
- High blood pressure
- An artery disease (carotid or peripheral)
- Heart disease
- High cholesterol levels
- Obesity or being overweight
- Family history
- Diabetes
- Atrial Fibrillation
- Physical Inactivity
- You’re older than 65
- A previous stroke or TIA
During a stroke screening session, the specialist will ask questions to uncover any of these risk factors. The doctor will also evaluate if you have any of the warning signs.
The following tests can be conducted to identify and prevent a stroke:
1. Carotid artery screening (ultrasound)
Carotid artery disease is one of the common risk factors for an ischemic stroke. Since the brain receives oxygen-rich blood from these arteries, any anomaly or obstruction is a big risk.
The specialist will use ultrasound to see the inside of your carotid arteries to identify any obstructions.
2. Brain CT scan
You’ve probably heard of this type of scan, which uses X-rays to scan your brain and visualize any signs of cell damage or bleeding.
3. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
This test can be done in addition to or instead of the brain CT scan. MRIs use magnetic fields and radio waves to visualize your entire body. This can help identify a clot or leakage.
4. Cerebral angiography
This stroke screening exam uses X-rays and an iodine contrast dye to relay images of blood vessels in the brain. It involves the insertion of a catheter (thin tube) into the arteries.
5. Atrial fibrillation screening
Atrial fibrillation, or an irregular heartbeat, is one of the more common stroke risk factors we mentioned. Depending on the specialists you choose for your stroke screening, this exam can be performed using an echocardiogram exam or electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG).
Other tests may include glucose screening, CTA and MRA tests, a platelet count or complete lipid screening.
Before your stroke prevention…
Patients who arrive at least 3 hours after identifying stroke symptoms experience less disability than those who arrive later. Early stroke screening tests can help prevent an attack and reduce your risk by identifying and managing potential risk factors. However, you must always consult qualified and experienced specialists before scheduling a screening.


 You suffer a stroke when your brain stops functioning partially or completely. A stroke is essentially an attack on the brain and is characterized by a lack of blood flow due to vessel blockage. When this happens, insufficient oxygen reaches the brain and brain cells start to die.
You suffer a stroke when your brain stops functioning partially or completely. A stroke is essentially an attack on the brain and is characterized by a lack of blood flow due to vessel blockage. When this happens, insufficient oxygen reaches the brain and brain cells start to die. There are various stroke screening tests that can be carried out to determine the likelihood of a possible attack. Most of these assessments are based on the patient’s risk factors. So, before we discuss the different tests, here are the major risk factors for a stroke:
There are various stroke screening tests that can be carried out to determine the likelihood of a possible attack. Most of these assessments are based on the patient’s risk factors. So, before we discuss the different tests, here are the major risk factors for a stroke:
