Pumping Blood With Congestive Heart Failure
 The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute defines congestive heart failure (sometimes known simply as heart failure) as the condition in which the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet a body’s needs.
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute defines congestive heart failure (sometimes known simply as heart failure) as the condition in which the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet a body’s needs.
This means your heart is unable to pump blood the way it should. Either your heart is not filling with enough blood or has trouble pumping blood to the rest of the body with enough force.
Although the terms “heart failure” and “congestive heart failure” are often used interchangeably, congestive heart failure typically refers to congestion in the body’s tissues. As blood flow out of the heart slows down, blood flow into the heart gets backed up and causes congestion.
The warning signs of heart failure
The most common signs of heart failure are:
- Shortness of breath, or trouble breathing (also known as dyspnea)
- Fatigue or feeling lightheaded
- Swelling in legs, ankles, and feet
These symptoms are most likely due to edema, which is a buildup of fluid in your body, such as in your lungs or tissues. Although swelling most often occurs in the lower parts of your body, it is possible that you may experience it in other parts of your body as well. You may also experience weight gain.
Other symptoms to look out for include persistent coughing, nausea or lack of appetite, confused or impaired thinking, and an increased heart rate.
If you experience one or more of these symptoms, please consult your doctor immediately. Your doctor may suggest you see a specialist, like the cardiologists at Manhattan Cardiology who are specially equipped to detect conditions such as heart failure.
The most common causes of heart failure
There are several conditions that can contribute to heart failure, including:
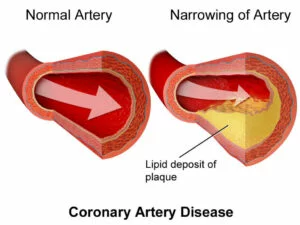
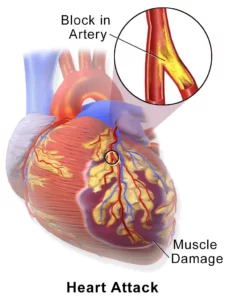 Coronary Heart Disease refers to the buildup of plaque in the heart’s arteries, which may contribute to high blood pressure and can lead to heart attacks.
Coronary Heart Disease refers to the buildup of plaque in the heart’s arteries, which may contribute to high blood pressure and can lead to heart attacks.
Note that unhealthy lifestyles will also increase your risk, especially if you have any of the listed conditions. Make sure you are getting enough physical activity and avoid smoking tobacco, drinking alcohol, using recreational drugs, and eating foods high in fat, sodium, and cholesterol. You are more likely to experience heart failure if you are overweight.
People who are 65 years or older have a higher risk of heart failure due to a weakening heart coupled with other medical conditions.
The treatment for congestive heart failure
The key to treating this condition is early detection and diagnosis through heart screening services. You may need to make lifestyle changes, take medications for congestive heart failure, or even receive surgery.
Possible medications may include:
- Nitrates
- Diuretics
- Vasodilators
- Beta blockers
- Inotropes
Many of these medications help relax your blood vessels, lower your blood pressure, and lessen the strain on your heart so it does not have to work as hard to pump blood.
Specifically, diuretics help your body get rid of sodium and water and reduce the swelling caused by edema. Beta blockers decrease your heart’s workload by slowing your heart rate and lowering your blood pressure.
As always, make sure to consult your doctor for the proper type of medication and choose a plan that is right for you.
In extreme cases or as your condition worsens, you may have to get a medical procedure or surgery. This may range from getting a pacemaker to a heart transplant for patients who have not responded to other forms of treatment or are at end-stage heart failure. Although not preferred, heart transplants may help prolong and improving your quality of life.
What to do if you or a loved one has heart failure
Located on the east side of Manhattan, Manhattan Cardiology offers world-class heart and vascular care and treatment. Our team of board-certified doctors will conduct a complete evaluation and provide a personalized plan of treatment.
Don’t let your heart failure go undiagnosed. Call Manhattan Cardiology at 212-906-7798 or request an appointment online.

 The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Coronary Heart Disease refers to the buildup of plaque in the heart’s arteries, which may contribute to high blood pressure and can lead to heart attacks.
Coronary Heart Disease refers to the buildup of plaque in the heart’s arteries, which may contribute to high blood pressure and can lead to heart attacks.

