National High Blood Pressure Education Month marks the “kickoff” of high blood pressure prevention and control activities for the year.
High blood pressure (HBP), affecting about 1 in 3 adults in the US, is a serious condition that can lead to coronary heart disease, heart failure, stroke, kidney failure, and other health problems.
“Blood pressure” is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps blood. If this pressure rises and stays high over time, it can damage the body in many ways.
There are many steps you can take to control/prevent high blood pressure.
Risk factors you CAN control are:
- Your medication. Talk with your doctor about any medication you are currently taking, and the risk of increased blood pressure.
- Your health. Certain health problems may increase blood pressure, such as Chronic Kidney Disease, Adrenal and Thyroid disorders.
- Your environment and habits. Lack of physical activity, high alcohol consumption, high sodium diet, smoking, and high stress level can all lead to a greater risk of heart disease.
Risk factors you CANNOT control are:
- Your age. The older you are, the higher your risk of increased blood pressure.
- Your race/ethnicity. Certain ethnicity groups, such as African Americans, have a greater risk of developing high blood pressure at an early age.
- Your family history. High blood pressure can run in families. Know your family history and take preventative measures early on if you are at risk.
The condition itself usually has no signs or symptoms. You can have it for years without knowing it. During this time, though, HBP can damage your heart, blood vessels, kidneys, and other parts of your body.
Knowing your blood pressure numbers is important, even when you’re feeling fine. If your blood pressure is normal, you can work with your Manhattan Cardiology health care team to keep it that way. If your blood pressure is too high, treatment may help prevent damage to your organs.
Blood Pressure Numbers
Blood pressure is measured as systolic (sis-TOL-ik) and diastolic (di-ah-STOL-ik) pressures. “Systolic” refers to blood pressure when the heart beats while pumping blood. “Diastolic” refers to blood pressure when the heart is at rest between beats. You most often will see blood pressure numbers written with the systolic number above or before the diastolic number, such as 120/80 mmHg. (The mmHg is millimeters of mercury—the units used to measure blood pressure.)
The table below shows normal blood pressure numbers for adults. It also shows which numbers put you at greater risk for health problems.
Categories for Blood Pressure Levels in Adults
(measured in millimeters of mercury, or mmHg)
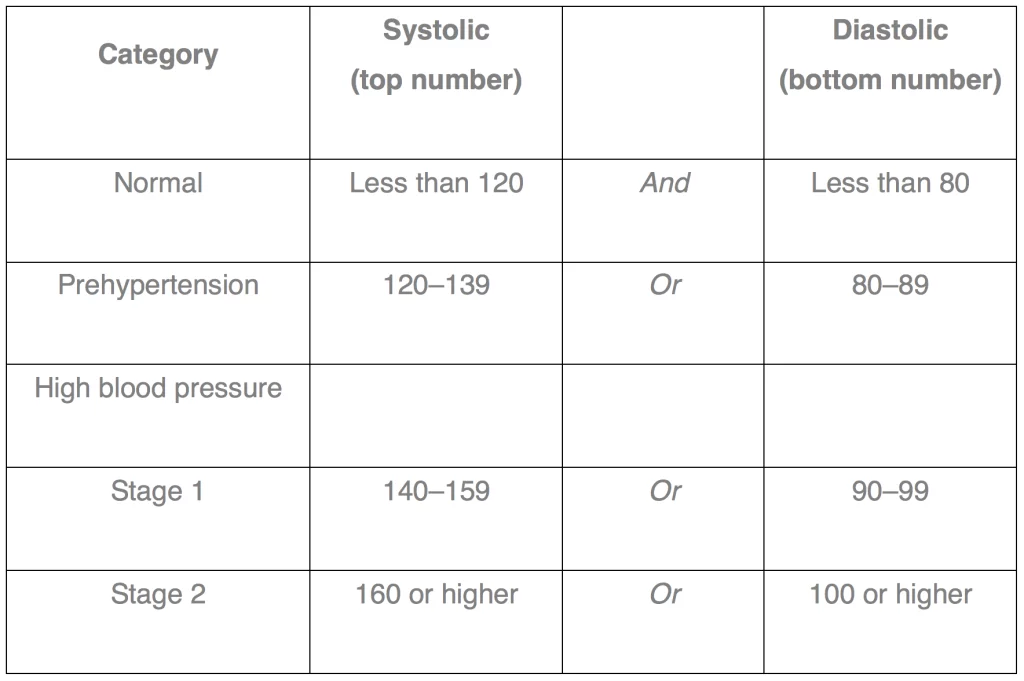
The ranges in the table apply to most adults (aged 18 and older) who don’t have short-term serious illnesses.
Blood pressure doesn’t stay the same all the time. It lowers as you sleep and rises when you wake up. Blood pressure also rises when you’re excited, nervous, or active. If your numbers stay above normal most of the time, you’re at risk for health problems. The risk grows as blood pressure numbers rise. “Prehypertension” means you may end up with HBP, unless you take steps to prevent it.
If you’re being treated for HBP and have repeat readings in the normal range, your blood pressure is under control. However, you still have the condition. You should see your doctor and follow your treatment plan to keep your blood pressure under control.
Your systolic and diastolic numbers may not be in the same blood pressure category. In this case, the more severe category is the one you’re in. For example, if your systolic number is 160 and your diastolic number is 80, you have stage 2 HBP. If your systolic number is 120 and your diastolic number is 95, you have stage 1 HBP.
If you have diabetes or chronic kidney disease, HBP is defined as 130/80 mmHg or higher. HBP numbers also differ for children and teens.
Manhattan Cardiology, in NYC, is here to help with high blood pressure treatment. Blood pressure is one of the easiest factors of your health to have screened and consistently monitored. If any of these risk factors pertain to you, make an appointment for an evaluation and any needed screening. It only takes a minute to check for high blood pressure and treating it immediately can reduce your risks for more serious problems in the future.



